communication
|
Learning Objectives:
|
Specification:
|
| 4.3_communication_starter_activity.docx | |
| File Size: | 37 kb |
| File Type: | docx |
| worksheet_for_communication.docx | |
| File Size: | 132 kb |
| File Type: | docx |
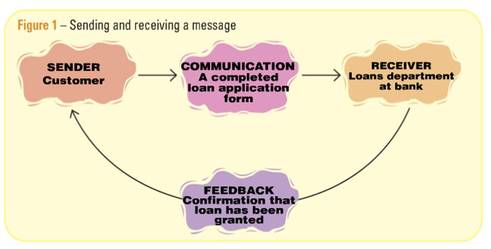
Key term: COMMUNICATION - Messages passed between a sender and a receiver, through a medium such as a letter or an email.
Key term: FEEDBACK - A response to a message by its receiver to the sender.
Key term: FEEDBACK - A response to a message by its receiver to the sender.
In order for communication to be effective, information must be:
- Simple
- Complete
- Clear
- Sent to the right people
- Sent through the appropriate communication channel
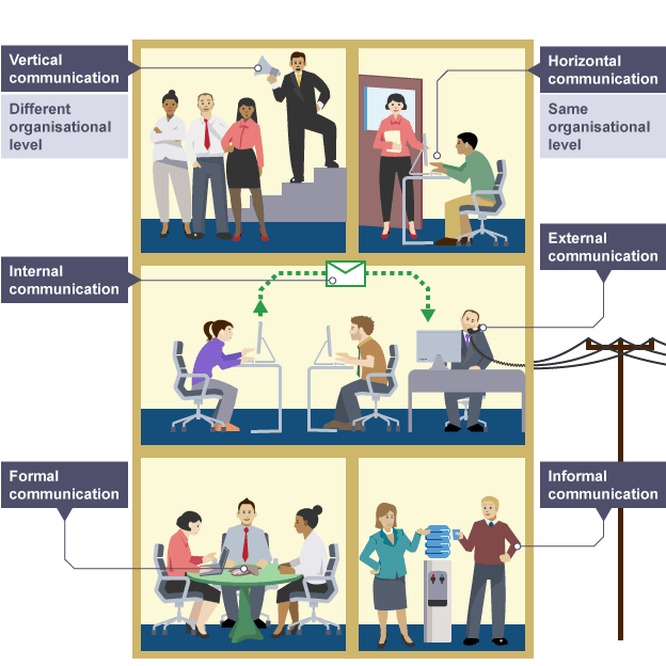
Key term: INTERNAL COMMUNICATION - Communication within the business organisation.
What examples of internal communication can you think of?
- a receptionist talking to another receptionist
- a manager sending an 'all staff' memo
- a director sending an email to his PA
- a document being sent from one branch to another
Key term: EXTERNAL COMMUNICATION - communication between the business and someone outside the organisation.
What examples of external communication can you think of?
- a customer services executive talking to a client
- a director speaking with a shareholder
- a building firm emailing a a bank regarding a quote for repairs
- an advert designed to interest potential customers
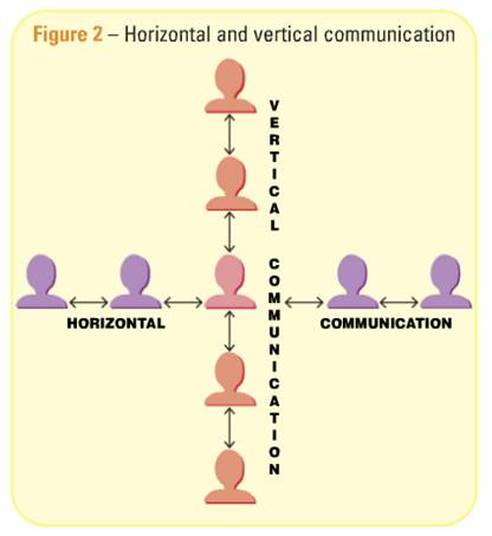
Key term: CHANNEL OF COMMUNICATION - the path taken by a message, such as horizontal communication, vertical communication or grapevine communication.
Key term: FORMAL CHANNELS OF COMMUNICATION - channels of communication that are recognised and approved by the business and by the employee representatives such as trade unions.
Information passes along channels of communication. These are channels which are recognised and approved by the business and by employee representatives such as trade unions. There are two main types of formal communication: horizontal and vertical communication.
Key term: VERTICAL COMMUNICATION - Communication up and down the organisational hierarchy.
Key term: HORIZONTAL COMMUNICATION - Communication between workers at the same level of the organisational hierarchy.
Often, communication does not get passed along official channels in an organisation. Informal communication is called communication through the grapevine. This could be referred to as 'gossip' when employees talk about the business to one another, if it is not directly to do with their job roles.
Key term: INFORMAL COMMUNICATION OR COMMUNICATION THROUGH THE GRAPEVINE - communication through channels that are not formally recognised by the business.
Channels of communication should be clearly laid down by a business. If they are not, then vital information can get sent to the wrong people, or get lost. Communication through the grapevine can sometimes be a problem because messages may get distorted and exaggerated the more people they go through. In general, the fewer the number of stages through which a communication passes (i.e. the shorter the chain of communication) the less likely a message will be misinterpreted.
There are a number of factors that make a communication effective:
- INFORMATION - the message being communicated must be accurate, complete and give all the relevant information. It must be simple and clear
- SENDER AND RECEIVER - the message must be sent from the right people, to the right people.
- TIME AND PLACE - Communication must take place at the right time and right place so that it is not useless
- METHOD - The method of communication must be right. E.g. an urgent notice about fire safety shouldn't be passed on by word of mouth
Barriers to communication
Not all communication is effective. There is a number of reasons why communication breaks down.
Not all communication is effective. There is a number of reasons why communication breaks down.
- Incorrect communication channel
- Poor communication skills or message not explained very well
- Lack of understanding (possibly through use of technological 'jargon')
- Messages can get distorted if they go through many people
- Technology breakdown
|
Benefits of good communication
|
Problems of poor communication
|